|
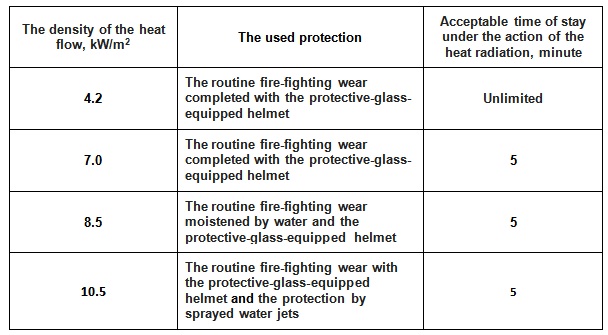
Protection against heat radiation has great importance to perform fire-fighting effectively. It is provided by the use of
the personal protective
equipment, which includes special clothes, a protective helmet, gloves, and boots. This routine fire-fighting wear of fireman completed with a
protective-glass-equipped helmet allows one to stay in the
zone of fire over a long period of time, if the density of the heat flow is less than
4.2 kW per square meter. The use of this fire-fighting wear and additional protective measures allows one to stay in the
zone of fire under the action of heat flow with higher
densities, but for a limited time.
Acceptable time of stay of fireman under the action of the heat radiation of fire
using the routine fire-fighting wear
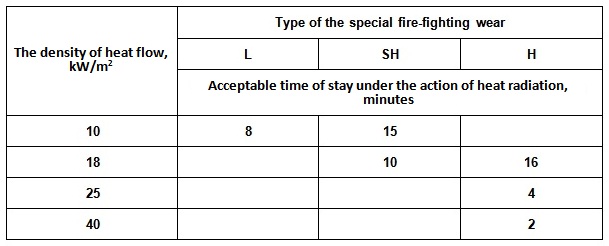
To protect fireman against heat flow with the density of more than
4.2 kW per square meter special
fire-protective wears, which are made of material with
a metallic coating, can be used: the means of local protection (type L, light),
the heat-reflecting
suite (type SH, semi-heavy), and the heat-protective
suite
(type H, heavy). With these special fire-fighting wears, the duration of stay under the action of heat radiation is also limited.
Acceptable time of stay of fireman under the action of heat radiation
using of special fire-fighting wears
Additional protection against heat radiation can be achieved by
the use of different screens. As protecting screens, water curtains produced by
fan sprayers,
as well as rigid screens in the form shields of different materials with a high coefficient of reflection of heat radiation are commonly used.
These curtains provide attenuation of heat radiation only in the 3.2-3.5 times. These
rigid screens have high screening capability, but they
are heated by acted heat radiation and not provide a high degree of protection over a long period of time.
From the
standpoint of degree of attenuation of heat radiation and duration of protection,
the screening of heat radiation by the screens “Sogda” and
the devises based on them is the most effective.
The figure shows the dependence of the density of
the heat flow as a function of distance to the mouth of
a gas-gusher with the height of 45 meters and the gas consumption of 58.6 cubic meters per second.
|

